In the heart of East Africa, Tanzania faces numerous public health challenges, exacerbated by a strained healthcare system and resource limitations. However, through work on the Chemonics co-implemented USAID flagship programs Frontier Health Markets (FHM) Engage and Human Resources for Health (HRH) in 2030, we have seen the power of strategic health initiatives towards addressing these issues and building sustainable health systems for the long term.
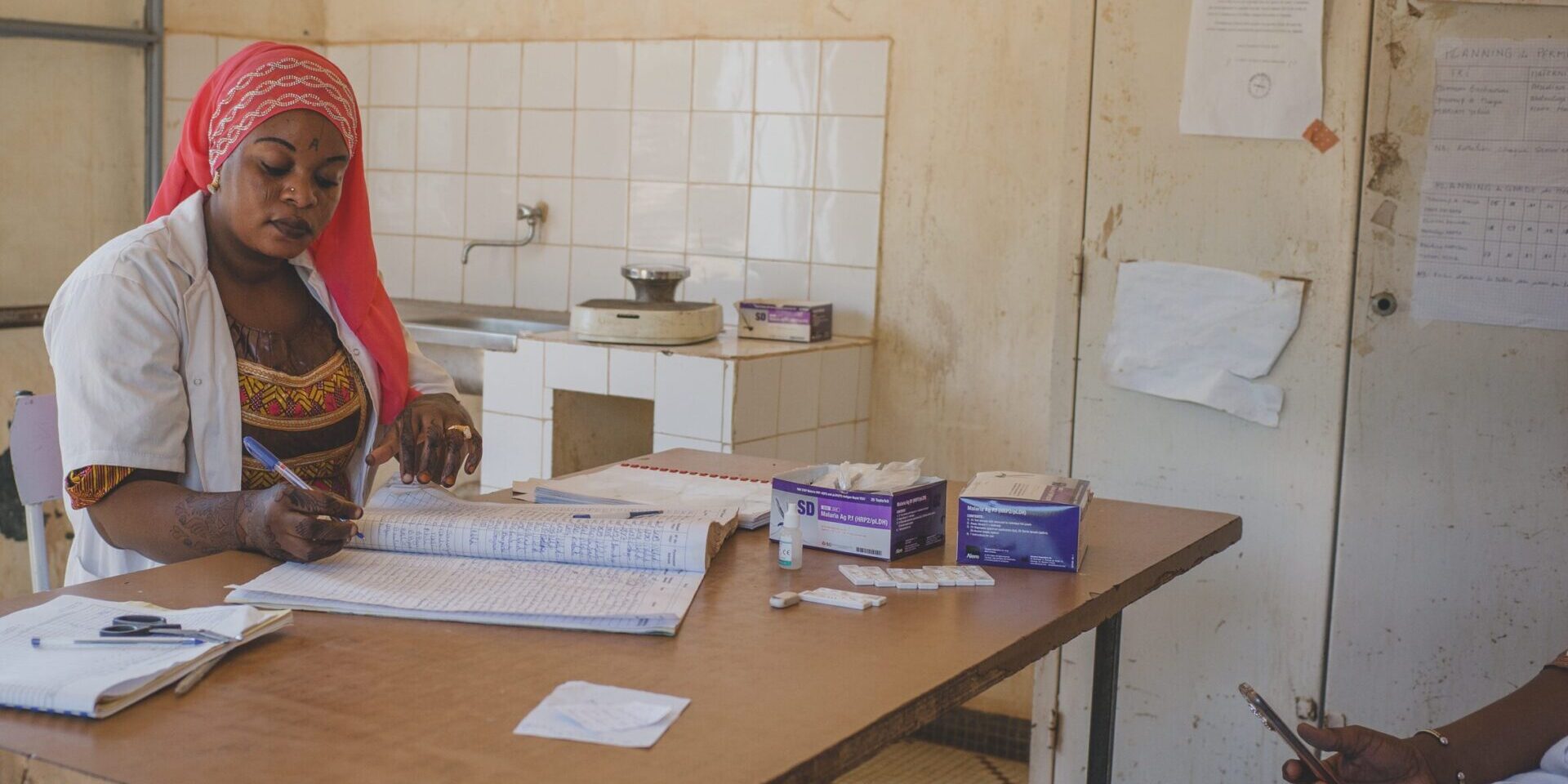
HRH2030 focused on bolstering the health workforce to deliver universal health coverage. One of HRH2030’s notable contributions was its support to the National One Health Platform, which enhanced the governance and leadership within the health sector, emphasizing zoonotic diseases. This initiative leveraged multisectoral collaboration, improving transparency and strengthening policies to better manage disease threats, aligning with the Global Health Security Agenda in Tanzania.
For example, in 2019, a scripted field simulation exercise at the Namanga One Stop Border Post, prompted by the 2018 Rift Valley Fever (RVF) outbreak, highlighted the importance of preparedness in preventing cross-border disease transmission. The exercise, involving health workers from Tanzania and Kenya, tested the functionality and readiness of existing outbreak protocols. The HRH2030 program played a crucial role in organizing this and other simulations, such as Ebola and avian influenza drills, which involved key stakeholders from diverse sectors such as public, plant, and animal health experts to strengthen the capacity of their national One Health platforms.
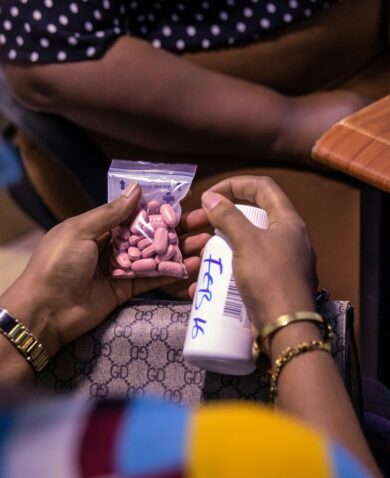
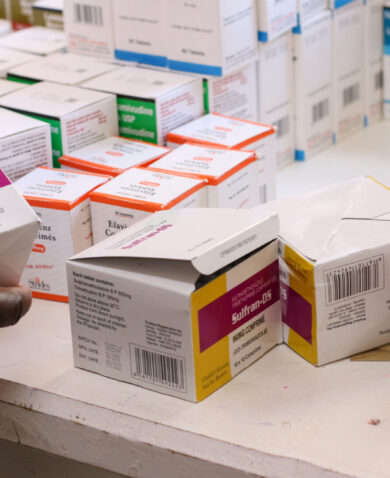
Meanwhile, FHM Engage’s approach is complementary, aiming to improve health markets in USAID priority countries, including Tanzania, through increased collaboration with the private sector. FHM Engage’s work in Tanzania, led by core consortium partner Results for Development with support from Chemonics, Pathfinder, and Zenysis Technologies, has improved local health markets by promoting equitable access to health products and services in the private sector. By applying a market development approach that engages local stakeholders in co-creating solutions to market failures, FHM Engage has helped improve access to essential health commodities such as HIV self-test kits and family planning products and services in Tanzania.
FHM Engage’s innovative strategies include the development of dashboards and private sector maps, tools that have enhanced how health commodities are distributed and accessed in Tanzania. These tools support data-driven decision-making, ensuring that health products meet the needs of diverse communities effectively. Additionally, FHM Engage’s collaboration with financial institutions has led to increased lending to health sectors, with loans amounting to over 70 billion Tanzanian shillings (approximately $23 million USD) in 2023. This financial mobilization supports healthcare providers in extending high-quality services to more Tanzanians, particularly in underserved areas.