Applying the Market Development Approach to Strengthen HIV Self-Testing Markets
August 16, 2023 | 3 Minute ReadAn Interview with Farhan Yusuf, Frontier Health Markets Engage Chief of Party, Tanzania
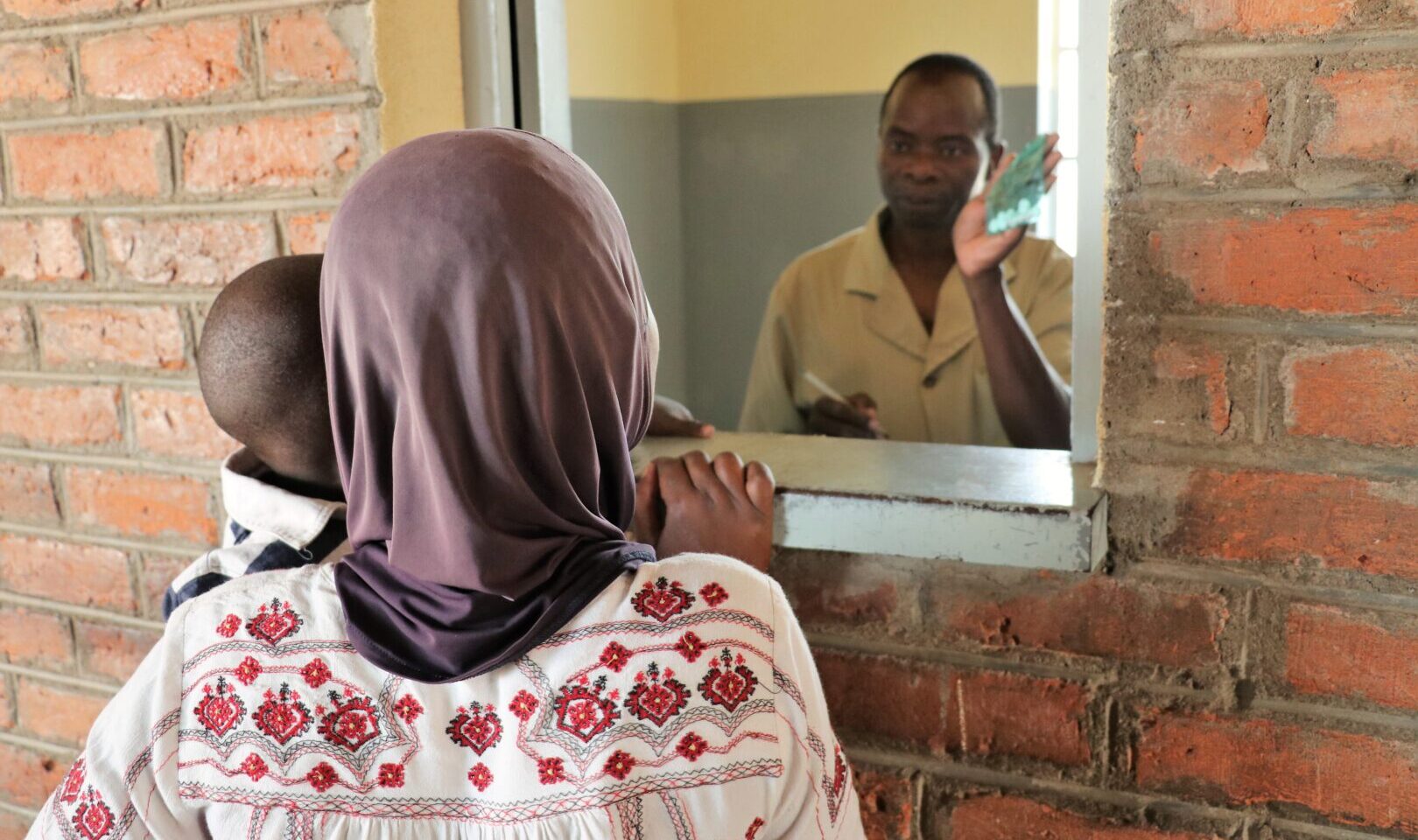
A market development approach (MDA) can be highly valuable in international development efforts, especially in the context of improving economic growth, poverty reduction, and sustainable development in low- and middle-income countries. With USAID’s flagship private sector health project Frontier Health Markets (FHM) Engage, Chemonics is excited to see how this approach can strengthen health markets and lead to improved health outcomes. In Tanzania, FHM Engage uses an MDA to strengthen the condom and HIV self-testing market systems to reduce the spread of HIV. We interviewed Farhan Yusuf, Chief of Party for FHM Engage in Tanzania and Program Director at Results for Development, to learn more about how this approach is applied to the HIV self-testing market there and the impact it has on communities that lack access to critical resources. The MDA involves a multi-stakeholder pathway that includes studying the interactions between private, public, and other actors, to identify opportunities for boosting supply and delivery frameworks in targeted regions.
Could you give us some more details on how the MDA works?
The MDA maps out all elements of market interactions across relevant market actors, thus providing a good overview of the problem statement and interactions. It has the explicit objective of creating more effective and more inclusive market systems and facilitating the role of development agencies in support of this by moving from traditional top-down technical assistance to market facilitation. This approach focuses on empowering market actors to design and deliver solutions and interventions that create effective and healthy markets for different products and services within different health areas by laying down a “pathway to impact” that involves the following stages: (1) diagnose, (2) design, and (3) deliver—while adapting and learning to maximize impact throughout the process.
How is this approach applied to the HIV self-testing market in Tanzania?
For HIV self-testing in Tanzania, FHM Engage conducted market scoping, and subsequently identified a group of different market actors from the public, private, and non-governmental sectors, and brought them together to discuss various elements of the market through a series of workshops that progressed on the pathway for impact previously mentioned.
How does this approach and its implementation differ from previous approaches used?
The MDA is a consultative process and requires collaboration with all the different market actors to co-create a vision for the market of a health product or service. It is strongly data driven. For HIV self-testing in Tanzania, the Market Development Group formed by FHM Engage developed a vision for the market where both oral and blood-based HIV self-testing kits are available with potential for other products, such as urine-based HIV self-test kits, to also be distributed when available. The HIV Self-Testing Implementation Framework developed by the Tanzania National AIDS Control Program determined the target groups and geographic areas for this implementation. The vision is to create an HIV self-testing market that is healthy and allows both public and private supply and delivery, along with supporting a total market approach that has public, socially marketed, and commercial products.
Keeping the total market in mind—free commodities from the public sector, subsidized commodities from the social marketing sector, and commercial products from the commercial sector—and leveraging insights from data enable one to think about the specific target groups and geographic areas to achieve maximum impact for those who need the health products and services the most. The challenge, however, is that since it is a systems approach the measurement is in the long term and may take some time. There are a lot of necessary pre-steps such as development of the right policies and guidelines needed before actual implementation. This is the path that FHM Engage has been taking in Tanzania.
Consumer choice often plays a key role in determining how health care resources are accessed. How does this factor influence the application of the MDA to the condoms and HIV self-testing markets in Tanzania?
The MDA works ideally through market development groups such as the one that was formed by FHM Engage in Tanzania. These groups must have market actors from both the public and the private sectors who can develop a vision for the market together. Insights and data from consumers about their preferences must be used in developing this vision and implementing the right interventions for a healthy market. We used various data sources, including work done by previous programs in the space, to understand consumer preferences and conduct our own rapid assessments with consumer target groups. We also included groups such as civil society organizations in our discussions to ensure that we can factor in the preferences of the consumers.
FHM Engage is a five-year cooperative agreement (7200AA21CA00027) funded by the United States Agency for International Development. We work to improve the market environment for greater private sector participation in the delivery of health products and services and to improve equal access to and uptake of high-quality consumer-driven health products, services, and information. Chemonics International implements FHM Engage in collaboration with Core Partners: Results for Development (co-technical lead), Pathfinder, Zenysis, and a group of 16 network implementation partners.